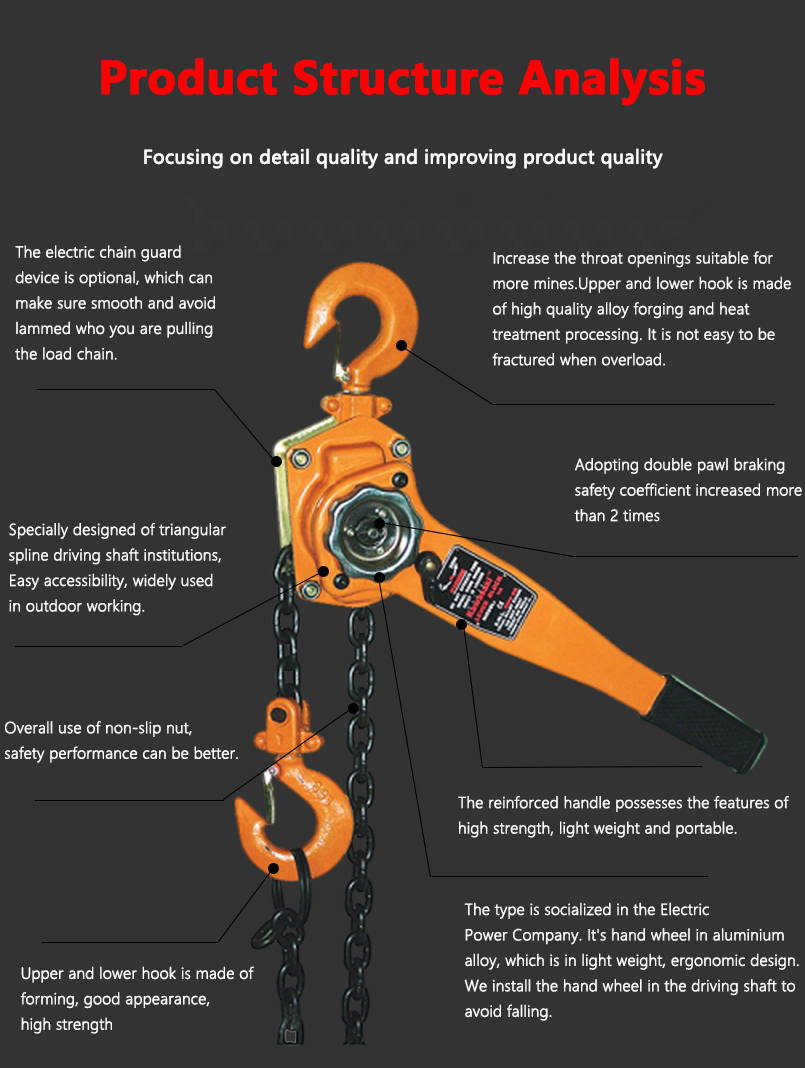
Introduction
Hand hoists, commonly used in industrial, construction, and mechanical applications, are essential tools for lifting and lowering heavy loads manually. These devices rely on a system of pulleys, gears, and chains to provide a mechanical advantage, allowing operators to handle substantial weights with minimal effort. Given the potential risks associated with their use, hand hoists are designed with various protection mechanisms to ensure safety, durability, and efficiency.
Key Protection Mechanisms
To enhance operational safety and prevent accidents, hand hoists incorporate multiple protection mechanisms. These mechanisms include load brakes, overload protection, safety latches, high-strength materials, and ergonomic designs.
1. Load Brake Mechanism
A load brake is a critical safety feature in hand hoists, ensuring that the load remains in place when lifting or lowering stops. The brake system generally consists of:
- Weston-Style Load Brake: This self-energizing brake uses friction discs and ratchet mechanisms to prevent unintended movement. When the operator stops pulling the chain, the brake automatically engages to hold the load.
- Friction Clutch: Some hoists use a friction clutch to provide smooth and controlled lowering, reducing wear on internal components and preventing sudden drops.
- Double Pawl Mechanism: To add redundancy, some hand hoists incorporate a double pawl system that ensures the brake remains engaged even if one pawl fails.
2. Overload Protection
Overloading a hoist beyond its rated capacity can cause mechanical failure, posing serious safety risks. Hand hoists often integrate overload protection features such as:
- Shear Pin Mechanism: In some hoists, a shear pin breaks if excessive force is applied, disconnecting the lifting mechanism and preventing damage.
- Slip Clutch: Some designs use a slip clutch that prevents further lifting if the load exceeds the safe limit, reducing stress on internal components.
- Load Limiting Devices: These devices alert the operator or automatically disengage the hoist when an overload condition is detected.
3. Safety Latches on Hooks
Hooks used in hand hoists are equipped with safety latches to prevent accidental detachment of the load. These latches work by:
- Spring-Loaded Mechanism: Ensuring that the hook remains securely attached to the load until manually disengaged.
- Heavy-Duty Construction: Made from reinforced materials to withstand impact and prevent deformation.
4. High-Strength Materials and Corrosion Resistance
Durability is an essential factor in hoist safety. High-quality hand hoists incorporate materials and coatings that enhance protection against environmental damage:
- Hardened Steel Components: Chains, gears, and hooks are often made from heat-treated or alloyed steel for superior strength.
- Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: Zinc or nickel coatings on chains and hooks prevent rust and degradation in harsh conditions.
- Sealed Bearings and Lubrication: Ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear and tear on moving parts.
5. Ergonomic and Safe Operation Design
Ergonomic features play a role in reducing operator fatigue and enhancing control:
- Comfortable Grip Handles: Rubberized or textured handles improve grip and control, reducing the risk of slippage.
- Smooth Chain Operation: Precision-machined gears ensure smooth pulling action, minimizing the effort required to lift loads.
- Reduced Kickback: Internal mechanisms help prevent sudden jerks or resistance that could cause injury.
6. Inspection and Maintenance Safety Features
To further enhance protection, many hand hoists include features that simplify inspection and maintenance:
- Visible Wear Indicators: Some models include markers on chains or load hooks to signal excessive wear.
- Easily Replaceable Components: Modular designs allow for quick replacement of worn parts, reducing downtime.
- Accessible Inspection Points: Covers and access ports facilitate regular maintenance checks without disassembly.
Conclusion
The protection mechanisms integrated into hand hoists are essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation. By incorporating load brakes, overload protection, safety latches, high-strength materials, ergonomic features, and maintenance-friendly designs, manufacturers significantly reduce the risk of accidents and prolong the lifespan of these critical lifting tools. Regular inspection and proper usage further enhance the safety and effectiveness of hand hoists in various industrial and construction applications.